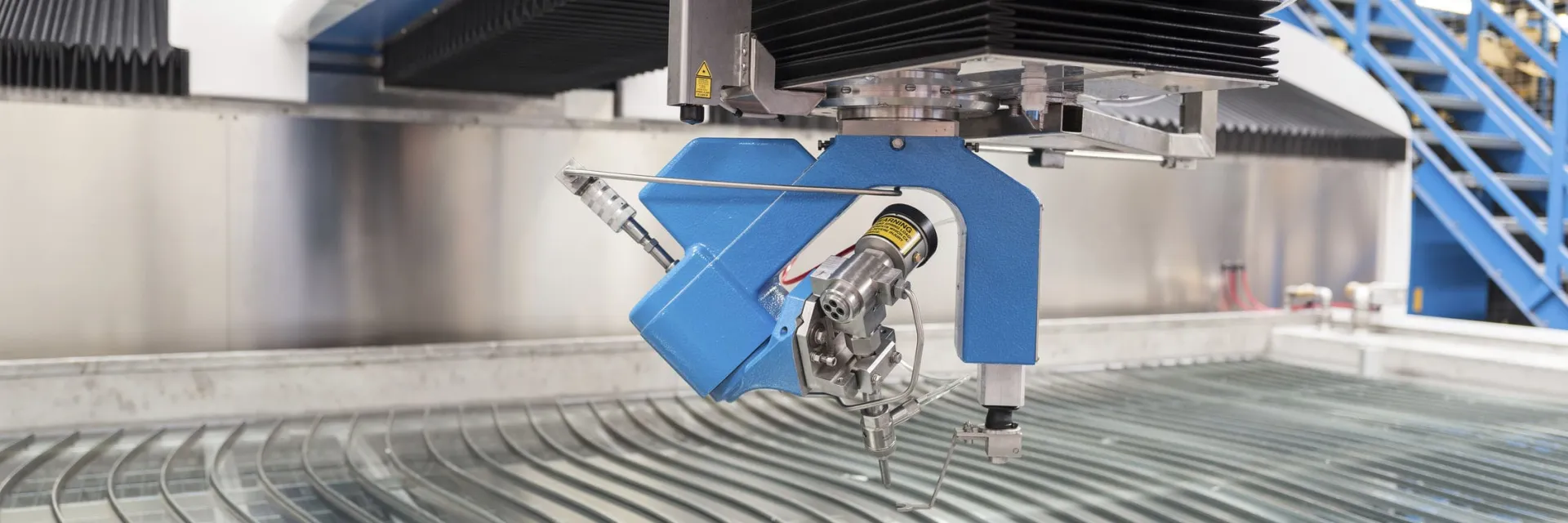
In the world of metal fabrication and precision cutting, two common methods stand out: waterjet cutting and plasma cutting. These techniques play a crucial role in shaping metals for various industries, each offering unique advantages and applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key differences between waterjet cutting and plasma cutting, helping you make an informed choice for your specific cutting needs.
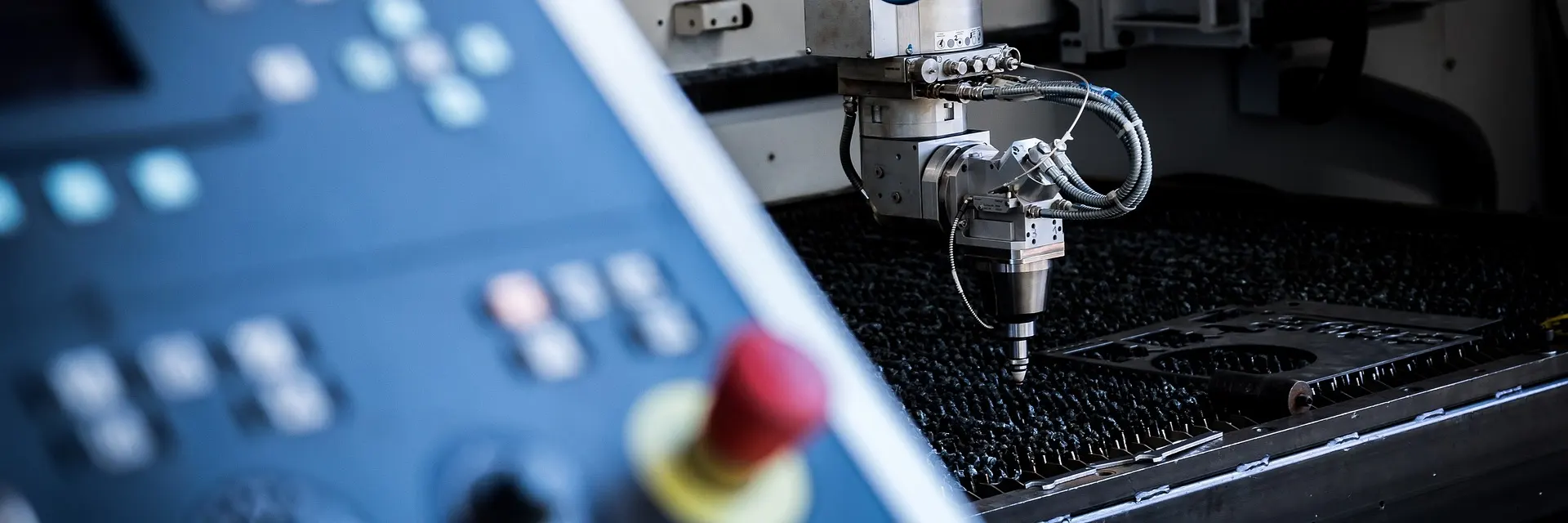

Introduction
Metal cutting is a fundamental process across industries, ranging from manufacturing and construction to aerospace and automotive. The choice between waterjet cutting and plasma cutting depends on factors like material type, thickness, precision, and budget. Let's explore the intricacies of both methods to help you decide which one suits your needs.
Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
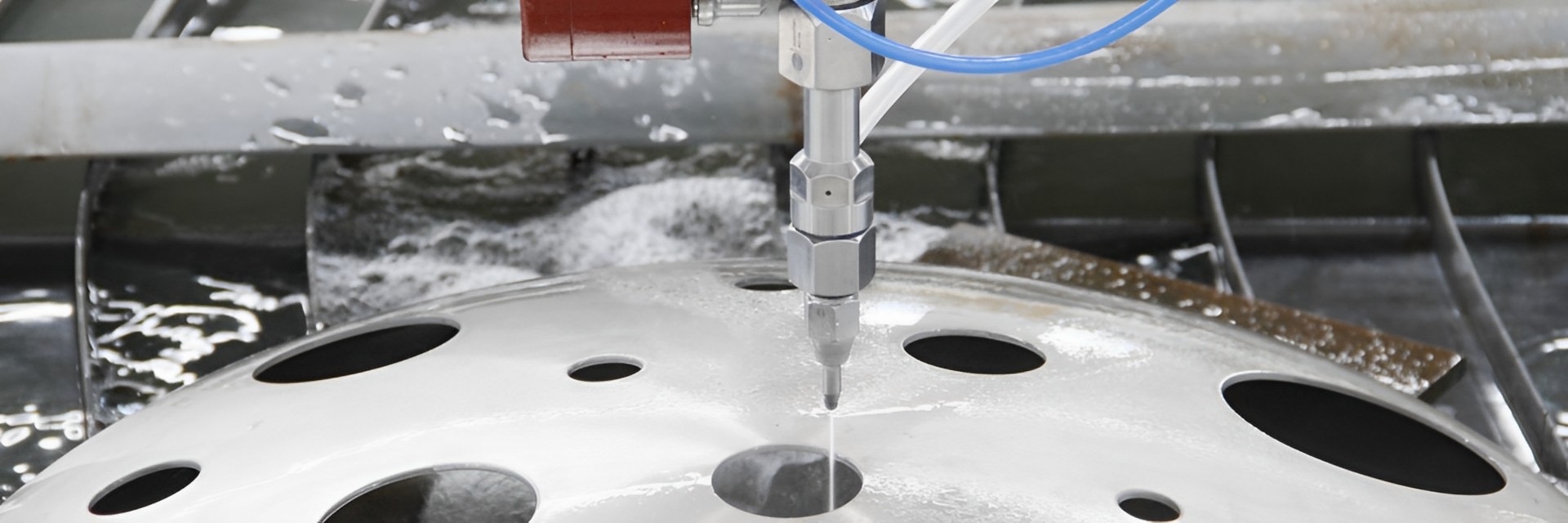
One significant advantage of waterjet cutting is that it produces minimal heat during the cutting process. This is crucial for materials that are sensitive to heat and can warp or lose their properties when exposed to high temperatures.

Maintenance Requirements
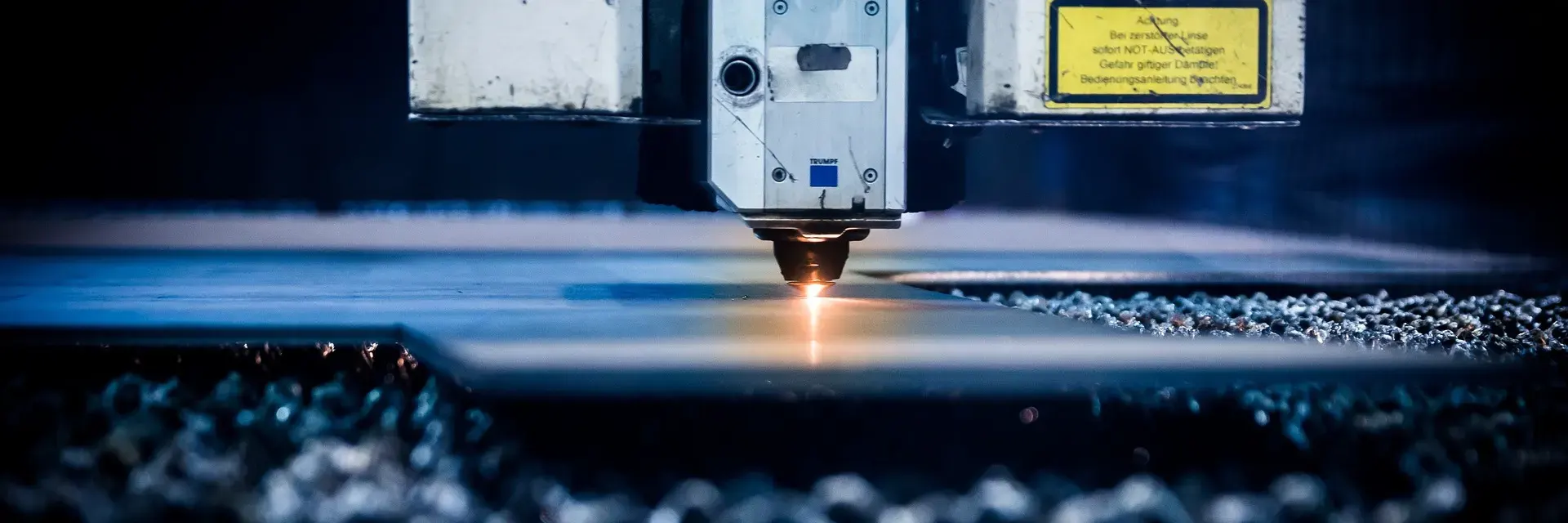
Waterjet cutting machines require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes abrasive replenishment and nozzle replacement. Plasma cutting machines also require maintenance, with a focus on keeping the torch consumables in good condition.Now that you have a better understanding of the differences between these two methods, you can make an informed decision based on your project's needs.

FAQs
Is waterjet cutting suitable for cutting heat-sensitive materials?Yes, waterjet cutting is ideal for heat-sensitive materials as it produces minimal heat during the cutting process.
Plasma cutting is generally faster due to its high cutting speeds.
Plasma cutting can produce fumes and gases, so proper ventilation and filtration are recommended.
While waterjet cutting equipment may be more expensive upfront, it can be cost-effective for certain applications due to its precision and versatility.





 NO.37 Tiancheng Road, Binjiang Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
NO.37 Tiancheng Road, Binjiang Development Zone, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China 電話/Whatsapp : +86-1377-0661-937
電話/Whatsapp : +86-1377-0661-937 Eメール : sales@comelycnc.com
Eメール : sales@comelycnc.com